UPnP & NAT-PMP¶
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) and NAT Port Mapping Protocol (NAT-PMP) are network services which allow software and devices to configure each other when attaching to a network. This includes automatically creating their own dynamic NAT port forwards and associated firewall rules.
The UPnP and NAT-PMP service on DefenseBolt, found at Services > UPnP & NAT-PMP, enables client PCs and other devices such as game consoles to automatically allow required inbound traffic.There are many popular programs and systems which support UPnP, such as Skype, uTorrent, mIRC,IM clients, Wii U, PlayStation 4, and XBox OneNAT- PMP is supported on Apple products. UPnP employs the Simple Service Discovery Protocol (SSDP) for network discovery, which uses UDP port 1900. The UPnP daemon used by DefenseBolt, miniupnpd , also uses TCP port 2189. When using a strict LAN ruleset, manually add firewall rules to allow access to these services, especially if the default LAN-to-any rule has been removed, or in bridged configurations. NAT-PMP is also handled by miniupnpd and uses UDP port 5351.
UPnP & NAT-PMP and IPv6 As of this writing, the UPnP and NAT-PMP service on current versions of DefenseBolt supports IPv6,but client support is still spotty.
Security Concerns UPnP and NAT-PMP are a classic example of the “Security vs. Convenience” trade- off. By their very nature,these services are insecure. Any program on the network can allow in and forward any traffic – a potential security nightmare. Onthe other side, it can be a choreto enter and maintain NAT port forwards and their associatedrules, especially when it comes to game consolesThere is a lot of guesswork and research involved to find the proper ports and settings, but UPnP just works and requires little administrative effort. Manual port forwards to accommodate these scenarios tend to be overly permissive, potentially exposing services that should not beopen from the Internet. The port forwards are also always on, where UPnP may be temporary. Access controls exist in the UPnP service configuration, which helps to lock down which devices are allowed to make alterations. Over and above the built-in accesscontrols, further control may be exerted with firewall rules. When properly controlled, UPnP can also be a little more secure by allowing programs to pick and listen on random ports, instead of always having the same port open andforwarded.
Configuration
To configure UPnP and NAT-PMP:
- Navigate to Services > UPnP & NAT-PMP
- Configure the options as follows:
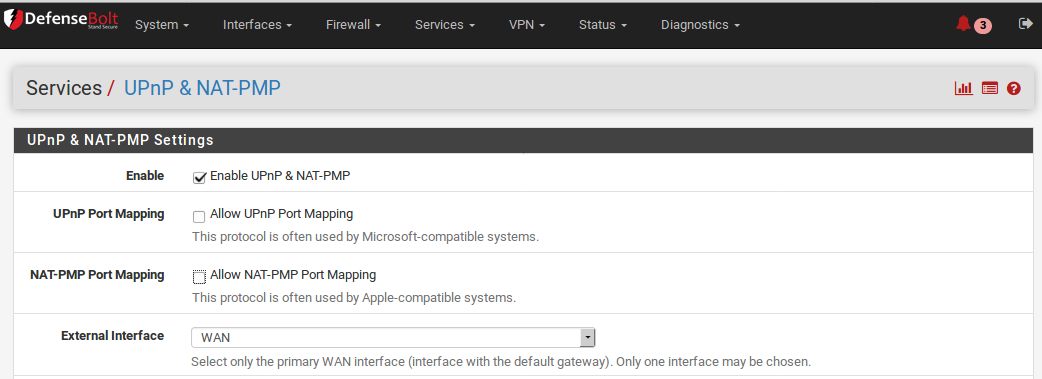
Enable UPnP & NAT-PMP Master control for the entire service. When unchecked, all of the sevices on this page are disabled.
Allow UPnP Port Mapping When checked, UPnP is allowed.
Allow NAT-PMP Port Mapping When checked, NAT-PMP is allowed.
External Interface The WAN interface for outgoing traffic. This must be set to the WAN containing the default gateway. Only one ExternalInterface may be selected.
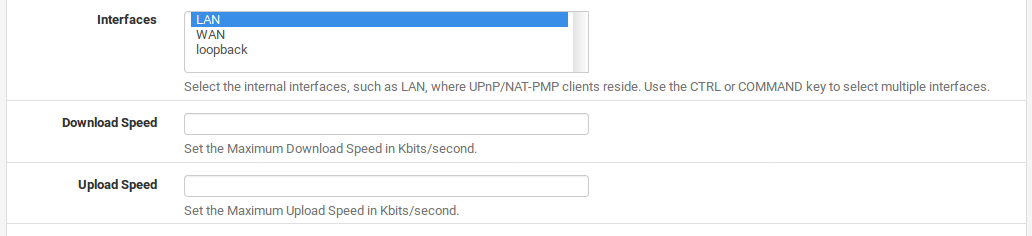
Interfaces The local interfaces where clients allowed to use UPnP/NAT-PMP reside. When a bridge is in use, only select the bridge interface with an IP address. Multiple interfaces maybe selected.
Download Speed Maximum download speed reported to clients, in Kilobits per second.
Upload Speed Maximum upload speed reportedto clients, in Kilobits per second.
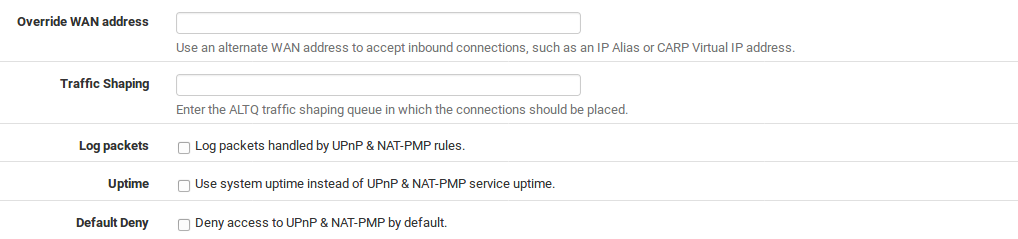
Override WAN Address Selects an alternate interface IP address to use, such as a CARP or IP Alias Virtual IP address.
Traffic Shaping Queue The name of an ALTQ (not Limiter) traffic shaping queue in which traffic allowed through using UPnP will be placed
Note
Exercize caution when selecting this queue. UPnP is used by traffic such as game consoles, which need high priority, and also by file transfer clients which may need low priority.
Log Packets When checked, port forwards generated by UPnP/NAT-PMP will be set to log, so that each connection made will have an entry in the firewall logs, found at Status > System Logs, on the Firewall tab.
Use System Uptime By default, the UPnP daemon reports the service uptime when queried rather than the system uptime. Checking this option will cause it to report the actual system uptime instead.
Deny Access by Default When checked, UPnP will only allow access to clients matching the access rules. This is a more secure method of controlling the service, but as discussed above,is also less convenient.
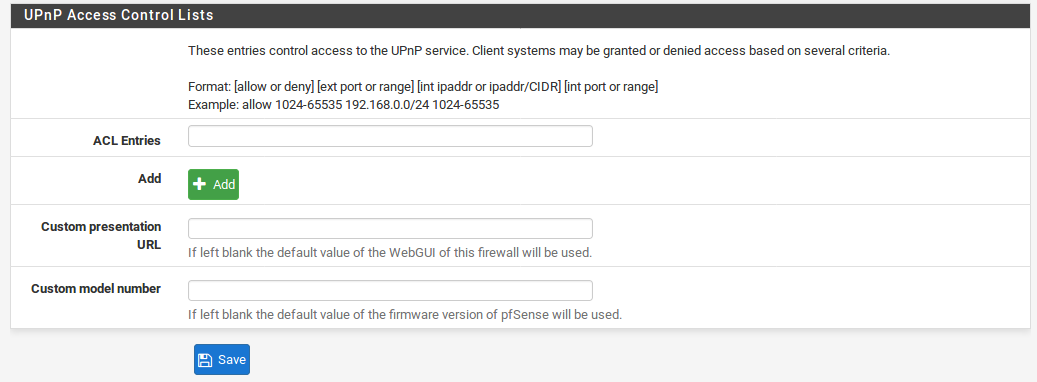
User Specified Permissions These fields specify user-defined access rules. If the defaultdeny option is chosen, rules must be set to allow access. Additional rules may be added by clicking Add Rules are formulated using the following format:
<[allow|deny]> <[external port|port range]> <[internal IP|IP/CIDR]> <[internal port|port range]>
- Click Save
The UPnP and/or NAT-PMP service will be startedautomatically.
UPnP User Permission Examples
Deny access to external port 80 forwarding fromeverything on the LAN, 192.168.1.1, with a /24 subnet, to local port 80:
| deny 80 192.168.1.1/24 80 |
Allow 192.168.1.10 to forward any unprivileged port:
| allow 1024-65535 192.168.1.10 1024-65535 |